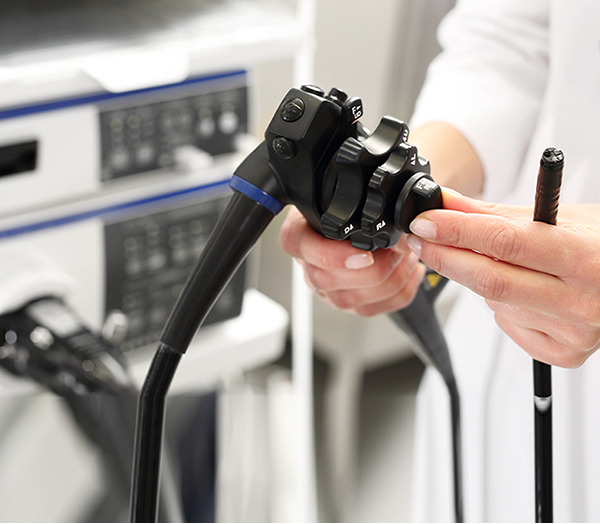
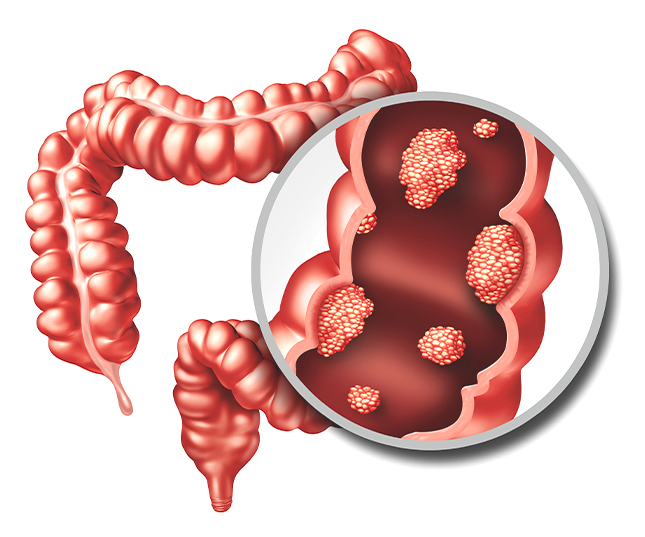
Doctors perform colonoscopy by using a specialised instrument called a colonoscope, which is a long, thin, and flexible tube. This instrument has a camera attached to the tip of the tube and is inserted through the anus and into the rectum so that the healthcare provider will have a clear view of the colon.
Colonoscopy is typically recommended for the following reasons:
Routine colonoscopies can help identify early signs of colorectal cancer, including precancerous polyps or other abnormalities, improving treatment and survival rates. For individuals with a family history of colorectal cancer or other risk factors, doctors may advise earlier and more frequent screenings to monitor for any recurrence or new growth.
A colonoscopy provides a detailed view of the colon to help identify possible sources of gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and chronic diarrhoea. Through direct visualisation of the colon lining, surgeons can diagnose various conditions, such as diverticulitis, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis.
If polyps are present, the surgeon will perform the necessary colonoscopy treatment in Singapore and remove these polyps to prevent them from potentially turning malignant (cancerous). Tissue samples may also be taken to test for the presence of cancerous cells. Sometimes, the surgeon can also treat blockages, stop internal bleeding, or extract a foreign object stuck in the colon through a colonoscopy.
- People who have any of the symptoms suggestive of colorectal cancer
- Bleeding
- Increasing constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Decrease in stool calibre
- Abdominal distension
- People who have a family history of colorectal cancer
- People who have a personal history of polyps
- People who are 50 years old and above
- Fasting for around six hours before the colonoscopy procedure
- Following a strict (generally bland, easy to digest) diet in the few days leading up to the procedure
- Stopping or adjusting certain medications as advised by their doctor
- Informing their doctor about any medication or medical history they may have
- Taking laxatives shortly before the colonoscopy (in order to empty the colon), as advised by their doctor
- Arrange for transportation home
- Sedation: An injection of sedatives will be given just before the start of the colonoscopy. This ensures patients will be in deep sleep throughout the procedure for a comfortable, pain-free experience.
- Insertion of the Colonoscope: The surgeon carefully inserts the colonoscope through the anus and into the colon. The camera at the end of the scope transmits real-time images onto a viewing monitor, allowing the surgeon to examine the colon lining closely.
- Colon Examination: As the colonoscope is manoeuvred through the colon, the surgeon can inspect all areas of the colon and detect any abnormalities found inside, such as polyps, malignant growths, or other signs of inflammation.
- Biopsies and Polyp Removal: Specialised instruments can be passed through the colonoscope, allowing the surgeon to collect tissue samples from suspicious areas. In some cases, any polyps found during the colonoscopy will be removed immediately (polypectomy).
- Completion: Once the examination is complete, the surgeon will gently withdraw the colonoscope from the patient’s body. The colonoscopy will take about 10 to 15 minutes to complete, although this may vary depending on the findings and interventions performed.
- Negative Result: A negative colonoscopy result means no abnormalities were found during the procedure. Doctors may advise low-risk patients to continue with their colonoscopy screenings every 10 years going forward.
- Positive Result: A colonoscopy result is considered positive if a polyp or any abnormalities are detected. In such cases, the doctor may perform further tests or additional treatments to address the underlying condition.
- Allergic response to the sedative used during the procedure
- Perforation or tear in the rectum or colon
- Faecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): This test detects blood in the stool that may not be visible to the naked eye, which may indicate the presence of colorectal cancer or large polyps. However, its results are less conclusive and is typically used as an initial screening tool.
- Virtual Colonoscopy: Also called CT colonography, this procedure uses advanced X-ray to generate detailed images of the colon and rectum. During the procedure, the colon will be inflated to visualise polyps and abnormal tissue better.
- Is colonoscopy painful?
A colonoscopy begins by first administering anaesthesia to the patient. This ensures that he or she is sedated during the whole procedure and thus would feel no pain or discomfort. Most patients wake up without having any memory of the colonoscopy taking place. - What is the typical recovery time after a colonoscopy?
Typically, recovery from a colonoscopy is quick with minimal downtime. Patients might feel slightly bloated but this will usually pass quickly. - What happens if you did not complete the bowel preparation?
Patients should inform their doctor if they do not complete the bowel preparation as the procedure may need to be rescheduled. Remember, if the colon is not clear, the scope cannot pass through the entire length of the colon. - Is it possible to have a colonoscopy without sedation?
A colonoscopy without sedation is possible, although it may be less comfortable. Some patients may prefer this approach to avoid the risks and side effects associated with sedation. Discuss your options and preferences with your colonoscopy doctor to determine the most appropriate method. - Is colonoscopy considered a day surgery?
Colonoscopy procedures in Singapore are typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home on the same day after a short observation.

Senior Consultant Colorectal & General Surgeon
MBBS (S’pore), MMed (Surgery), FRCS (Edinburgh), FAMS (General Surgery)
With over two decades of experience, Dr Ng Kheng Hong is skilled in providing effective colonoscopies to detect and manage colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal conditions. He previously served as the Director of Minimally Invasive Surgery at the Department of Colorectal Surgery at the Singapore.